LSST will have a presence at the January 2012 meeting in Austin, starting with a half-day "splinter meeting" in the Austin Convention Center on Sunday afternoon, January 8th. The ten coordinated posters in LSST session 156 will be up for one day, Monday, January 9th. An LSST booth in the exhibit hall will also be up throughout the meeting.
Poster Session
156.02 Developments in Telescope & Site
Victor Krabbendam1 , William J. Gressler1, John R. Andrew1, Jeffrey D. Barr1, Charles F. Claver1,2, Joe DeVries1, Edward Hileman1, Ming Liang1, Douglas R. Neill1, Jacques Sebag1, Srinivasan Chandrasekharan1, Amali Vaz3, Oliver Wiecha1, Bo Xin4 and the LSST Collaboration
1National Optical Astronomy Observatory, 2Large Synoptic Survey Telescope, 3Harvard Univ., 4Purdue Univ.
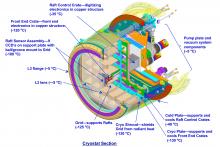
156.04 Image Quality and Performance of the LSST Camera
D.K. Gilmoreǂ, S. Kahnǂ, A. Rasmussenǂ, J. Singalǂ, and the LSST Camera Teamǂ
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory / Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology
156.06 Mapping the Stellar Content of the Milky Way with LSST
John Bochanski1, Paul Thorman2, Kevin Covey3, Knut Olsen4, Saurav Dhital5, Timothy C. Beers4, Pat Boeshaar2, Phillip Cargile5, Márcio Catelan8, Seth Digel7, Puragra Guhathakurta8, Todd Henry9, Zeljko Ivezic10, Mario Juric11, Jason Kalirai12, J. Davy Kirkpatrick13, Peregrine M. McGehee13, Dante Minniti6, Anjum Mukadum10, Joshua Pepper5, Andrej Prsa14, Rok Roskar15, J. Allyn Smith16, Kevian Stassun5, Anthony Tyson2 and the LSST Stellar Populations and Milky Way and Local Volume Science Collaborations
1The Pennsylvania State Univ., 2Univ. of California - Davis, 3Lowell Observatory, 4National Optical Astronomy Observatory , 5Vanderbilt Univ., 6Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, 7KIPAC/SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, 8UCO/Lick Observatory,
156.08 LSST Image Simulations
John R. Peterson1, J. G. Jernigan2, A. J. Connolly3, Z. Ahmad1, J. Bankert1, D. Bard4, C. Chang5, R. R. Gibson3, D. K. Gilmore4, E. Grace1, M. Hannel1, M. Hodge1, L. Jones3, S. M. Kahn4, K. S. Krughoff3, S. Lorenz1, S. Marshall4, S. Nagarajan1, E. Peng1, A. Rasmussen4, M. Shmakova4, N. Silvestri3, N. Todd1, M. Young1
1Purdue Univ., 2Univ. of California - Berkeley, 3Univ. of Washington, 4SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, 5Stanford Univ.
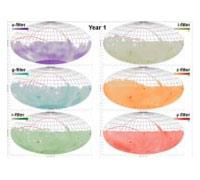
156.10 Evaluating LSST Schedule Realizations
Srinivasan Chandrasekharan1, Stephen T. Ridgway1, Kem H. Cook2, Cathy E. Petry3, R. Lynne Jones4, Simon K. Krughoff4, Zeljko Ivezic4
1National Optical Astronomy Observatory, 2Large Synoptic Survey Telescope, 3Univ. of Arizona, 4Univ. of Washington